Highlights
- Food authenticity ensures that a food product is genuine, accurately labeled, and free from adulteration or tampering.
- Various methods like organoleptic testing, chemical analysis, and DNA testing are used to verify food authenticity and detect fraud.
- Food authenticity is crucial for food safety, quality assurance, and maintaining consumer trust in the food industry.
- Common food authenticity issues include misrepresentation of geographical origin, ingredient substitution, and adulteration with cheaper or unauthorized additives.
- Ensuring food authenticity requires a combination of analytical techniques, industry knowledge, and fraud detection abilities.
- Ensuring food authenticity benefits public health, consumer confidence, fair competition, regulatory compliance, and transparency in the food supply chain.
Food authenticity refers to the concept that a food product is genuine and true to its nature, and that it has not been adulterated or tampered with in any way. This includes ensuring that the food product is accurately labeled and that it contains only the ingredients and additives that are listed on the label.
This can be verified through various methods such as organoleptic testing, chemical analysis, and DNA testing. These methods can be used to identify and authenticate the food product, and to detect any fraud, substitution or adulteration.

The concept of food authenticity is particularly important in the context of food safety and quality assurance, as it ensures that consumers are getting what they paid for, and that the food product does not pose a health risk.
It is also important for protecting the reputation of a food product, and for maintaining consumer trust in the food industry.
Food safety knowledge is for all!

Every consumer deserves to have high quality and safe food. …Read more!

Some specific examples of food authenticity issues are:
- Misrepresentation of geographical origin of food products
- Substitution of ingredients in food products
- Adulteration of food products with cheaper ingredients or non-authorized additives
- Misrepresentation of the composition, quality or characteristics of a food product
- Misrepresentation of the nutritional or health-related claims of a food product
Ensuring food authenticity can be challenging, as it requires a combination of different analytical techniques, a good knowledge of the food industry and the ability to detect fraud. There are different regulations, laws and standards in place around the world to ensure food authenticity, but it’s important for food industry, governments, and consumers to work together to ensure that food products are safe, authentic and accurately labeled.
Read about food traceability here!
Food adulteration as a food authenticity issue
Food adulteration is the act of intentionally adding harmful, inferior, or cheaper substances to a food product, or removing valuable or essential components of a food product, with the intention of deceiving consumers and/or increasing profits. This is often done without the knowledge or consent of consumers, and it can pose serious health risks.
Food adulteration examples
Food adulteration can involve a wide range of practices, including adding water, chemicals, or other substances to a food product, replacing expensive ingredients with cheaper ones, diluting a food product with fillers or extenders, or using outdated or contaminated ingredients.
Food adulteration can occur at any point in the food supply chain, from the farm to the consumer. It can be done by producers, manufacturers, distributors, or retailers, and it can be intentional or unintentional. Commonly adulterated foods include spices, dairy products, meat, seafood, and honey, but virtually any food product can be subject to adulteration.
The consequences of food adulteration
The consequences of food adulteration can be serious, ranging from mild illnesses to severe food poisoning and even death. Food adulteration can also have negative economic and social impacts, such as loss of consumer confidence, damage to the reputation of the food industry, and unfair competition.
Summary of specific methods for testing for authenticity of food
There are several methods for testing the authenticity of food. Some of the most common methods include:
- DNA testing: This method involves analyzing the DNA of a food product to determine its species or variety. DNA testing can help to detect adulteration or substitution of a food product with a different species or variety. This method is commonly used for meat, fish, and plant-based products.
- Stable isotope analysis: This method involves analyzing the stable isotopes of elements in a food product, such as carbon or nitrogen, to determine its origin or authenticity. This method can help to detect fraud or mislabeling of a food product, such as falsely claiming it is organic or from a specific geographic region.
- Spectroscopy: Spectroscopy is a method that uses light to analyze the chemical composition of a food product. Different types of spectroscopy, such as infrared spectroscopy or mass spectrometry, can be used to detect contaminants, adulterants, or other substances that are not supposed to be in a food product.
- Chemical analysis: Chemical analysis involves testing the chemical properties of a food product, such as its pH or water activity, to determine its authenticity. This method can help to detect the addition of fillers, diluents, or other substances that are not supposed to be in a food product.
- Sensory analysis: Sensory analysis involves using human senses, such as taste, smell, and sight, to evaluate the quality and authenticity of a food product. This method can be subjective, but it can be useful for detecting changes in a food product that may indicate fraud or adulteration.
- Microscopy: Microscopy involves using a microscope to examine the physical properties of a food product, such as its structure and texture. This method can help to detect the addition of fillers, extenders, or other substances that are not supposed to be in a food product.
- Electrochemical methods: Electrochemical methods involve measuring the electrical properties of a food product to determine its composition or authenticity. For example, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy can be used to detect the presence of contaminants or adulterants in a food product.
- Chromatography: Chromatography is a technique used to separate and analyze the different components of a mixture. Different types of chromatography, such as gas chromatography or liquid chromatography, can be used to detect adulterants or contaminants in a food product.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): ELISA is a method that uses antibodies to detect specific proteins or other molecules in a food product. This method can be used to detect the presence of allergens or other proteins that are not supposed to be in a food product.
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy: NMR spectroscopy is a method that uses magnetic fields to analyze the chemical structure of a food product. This method can be used to detect the presence of contaminants or adulterants in a food product.
- Fluorescence spectroscopy: Fluorescence spectroscopy involves measuring the fluorescence of a food product to determine its composition or authenticity. This method can be used to detect the presence of additives or other substances that are not supposed to be in a food product.
- Isotope ratio mass spectrometry (IRMS): IRMS is a method that measures the isotopic composition of elements in a food product, such as carbon, nitrogen, or oxygen. This method can be used to determine the geographic origin or authenticity of a food product, as well as to detect the addition of synthetic compounds.
Overall, these methods can be used alone or in combination to test the authenticity of a food product. The choice of method will depend on the type of food being tested and the specific characteristics being evaluated.
Potential benefits of ensuring food authenticity
Ensuring food authenticity can provide several benefits. Here are some potential benefits of ensuring food authenticity:
- Protection of public health: Authenticity testing can help to detect food fraud and protect public health by identifying potentially harmful substances or allergens in food. This can prevent the spread of foodborne illnesses and protect vulnerable populations.
- Consumer confidence: Accurate food labeling builds consumer trust and confidence in the food supply, which can have positive effects on sales and brand reputation. When consumers know that they are getting what they paid for, they are more likely to return to that brand and recommend it to others.
- Fair competition: Ensuring food authenticity promotes fair competition in the food industry. When one company fraudulently labels a product, they can undercut their competitors and gain an unfair advantage. Authenticity testing helps to level the playing field and promote competition based on quality, rather than deception.
- Regulatory compliance: Food authenticity testing can help food producers and distributors to comply with food safety regulations, such as labeling requirements and country-of-origin labeling. Compliance with regulations can prevent legal consequences, such as fines, penalties, and lawsuits.
- Transparency and traceability: Ensuring food authenticity promotes transparency and traceability in the food supply chain. This can help to identify the source of contamination or fraud and prevent it from happening again in the future. It also enables consumers to make informed choices about the food they purchase.
How food processors can ensure authenticity for their food products
Food processors can ensure food authenticity by implementing several measures, including:
- Quality and safety management systems: Implementing a quality management system, such as ISO 22000 or FSSC 22000, can help food processors to identify and prevent potential authenticity risks throughout the production process.
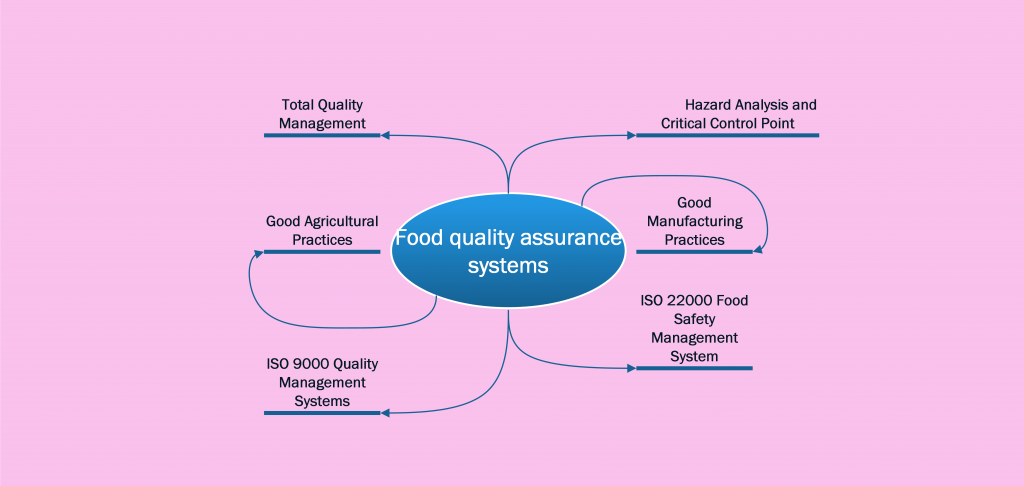
- Ingredient traceability: By keeping detailed records of the origins and suppliers of all ingredients used in their products, food processors can ensure that their products are authentic and free from contaminants or substitutions.
- Testing and analysis: Food processors can use a variety of analytical techniques to test the quality of their products, including DNA-based methods, isotope ratio analysis, and chemical fingerprinting.
- Third-party certification: Third-party certifications, such as organic, non-GMO, or fair trade, can provide an additional level of assurance that products are authentic and have been produced according to specific standards.

- Compliance with regulations: Food processors should comply with all relevant food authenticity regulations and guidelines, such as the EU Regulation No. 1169/2011 on the provision of food information to consumers.
- Auditing: Auditing of suppliers and production facilities can help to ensure that ingredients and products are authentic and meet the required standards.
- Consumer complaints and recall management: Having a system in place to manage consumer complaints and recall in case of authenticity issues, is important for the food industry.
By implementing these measures, food processors can ensure that their products are authentic and meet the expectations of consumers and regulators.
How can consumers protect themselves from food fraud?
Here are some ways in which consumers can protect themselves from food fraud:
- Buy from reputable sources: Purchase food products from reputable and trustworthy sources, such as reputable retailers or manufacturers. Look for companies with good reputations for quality and authenticity, and avoid purchasing from unknown or unverified sources.
- Read labels carefully: Read the labels on food products carefully to look for any suspicious or unfamiliar ingredients, and to ensure that the product is what it claims to be. Be wary of products that claim to be “all natural” or “organic” without any certification or verification.
- Check the packaging: Check the packaging of food products for any signs of tampering or damage, and avoid purchasing products with damaged, broken, or opened seals.
- Know the source: Try to learn more about the source of the food product, such as where it was produced or grown, and how it was transported and stored. Be wary of food products that come from unknown or unverified sources, or from countries with lower food safety standards.
- Be aware of common frauds: Be aware of common food frauds, such as mislabeling, substitution, or dilution, and learn how to identify the signs of these frauds. For example, if a food product has an unusually low price or claims to be a rare or exotic ingredient, it may be a sign of fraud.
- Report suspicious activity: If you suspect that a food product may be fraudulent, report it to the appropriate authorities, such as local health or consumer protection agencies, or the manufacturer or retailer of the product.
- Be wary of online purchases: If purchasing food products online, be cautious and purchase from reputable and trusted retailers. Avoid purchasing from unknown or unverified sources, and be sure to read reviews and check for any red flags, such as unusually low prices or poor customer reviews.
- Check for certifications: Look for food products that have been certified by a recognized third-party certification program, such as the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), the Safe Quality Food (SQF) Program, or the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system. These certifications indicate that the product has been rigorously tested and meets high safety and quality standards.
- Stay informed: Stay up-to-date on food safety and fraud issues by following trusted sources of information, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), or the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- Be vigilant when traveling: When traveling, be cautious about purchasing food products from street vendors or unfamiliar locations. Stick to reputable restaurants and food markets, and be sure to wash or peel fruits and vegetables before consuming.
- Pay attention to storage and handling: Proper storage and handling of food products can help prevent food fraud and contamination. Be sure to store food products at the appropriate temperatures, avoid cross-contamination, and follow safe food handling practices, such as washing hands before handling food.
By taking these steps, consumers can help protect themselves from food fraud and ensure that the food products they consume are safe, authentic, and of high quality.
Source of cover image in this article.
You can also watch instead of reading!
Our Blog ↗
Read the latest from our blog
Ask a Question ↗
Ask a question and get answers from our community
Give Feedback ↗
We value your feedback.



