Highlights
- Animal by-products are parts of animals that are not typically consumed as food but can be used for various purposes.
- Animal organs can be consumed by humans or used in pet food.
- Animal by-products can be classified as edible or non-edible, depending on their suitability for human consumption.
- Ensuring complete value addition of animal by-products reduces waste, improves efficiency, maximizes profits, and provides valuable resources.
- Failure to ensure complete value addition of animal by-products can result in environmental pollution, economic losses, animal welfare concerns, health risks, wasted potential as food sources, increased greenhouse gas emissions, decreased food security, and reduced quality of life.
Animal by-products are the parts of an animal that are not typically consumed as food, but can still be utilized for a variety of purposes. These by-products can include:
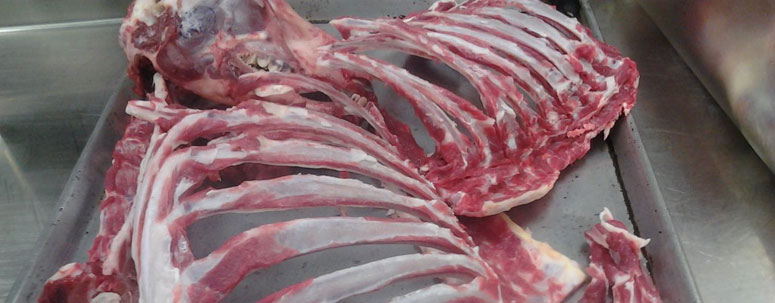
- Bones: Animal bones can be used to produce bone meal, which is a valuable source of calcium and other minerals for plants. Bone meal is commonly used as a fertilizer in agriculture.
- Skin and hides: Animal hides can be tanned and turned into leather, which is used in a variety of products such as shoes, belts, and jackets. Animal skins can also be used to produce gelatin, which is used in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
- Fat: Animal fat can be used to produce soap, candles, and other products. It can also be used as a source of energy, such as in the production of biodiesel.
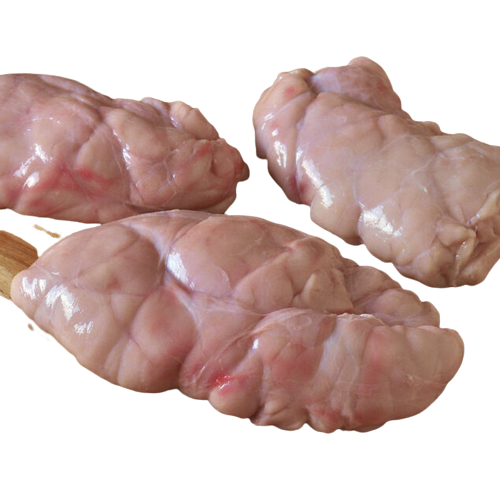
- Organs: Animal organs such as liver, heart, and kidneys can be used for human consumption, as well as for pet food.
- Blood: Animal blood can be used to produce blood meal, which is a rich source of nitrogen for plants. Blood meal is often used as a fertilizer in agriculture.
- Feathers: Animal feathers can be used to produce down, which is used in pillows, comforters, and other bedding products.
Overall, animal by-products are a valuable resource that can be utilized in a variety of ways. By making use of these by-products, we can reduce waste and make our use of animals more efficient and sustainable.
Categories of animal by products
Animal by-products can be classified into edible and non-edible categories, based on whether or not they are suitable for human consumption.
Edible by-products are those that are safe and suitable for human consumption. These by-products include meat, liver, heart, and other internal organs that are commonly consumed as food in many cultures around the world.
Non-edible by-products, on the other hand, are those that are not suitable for human consumption, but can still be utilized in other ways. These by-products include bones, hides, skins, and other parts of the animal that are not typically consumed as food. Non-edible by-products can be used in various industries, including leather production, pet food manufacturing, and fertilizer production.
Food safety knowledge is for all!

Every consumer deserves to have high quality and safe food. …Read more!


Here is a list of common edible by-products that are derived from animals:
- Beef: Liver, heart, kidney, tongue, oxtail, tripe, and bone marrow.
- Pork: Liver, heart, kidney, tongue, ears, snout, and trotters.
- Lamb: Liver, heart, kidney, and tongue.
- Poultry: Liver, heart, gizzard, and feet.
- Fish and seafood: Fish roe, liver, and milt.
- Game meats: Liver, heart, kidneys, tongue, and bone marrow.

Here is a list of common non-edible by-products that are derived from animals:
- Hides and skins: These are used to produce leather and are a valuable raw material for the clothing and footwear industries.
- Bones: These can be used to produce bone meal, which is a valuable source of calcium and other minerals for plants. Bones can also be used in the production of gelatin, which is used in a variety of products, including food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
- Hooves and horns: These are used to produce gelatin, glue, and fertilizer.
- Feathers: These are used in the production of down and feather pillows and comforters.
Importance of ensuring complete value addition of all animal by-products – no waste
It is important to ensure complete value addition of all by-products derived from animals for several reasons:
- Reducing waste: By utilizing all parts of an animal, we can reduce waste and minimize the environmental impact of animal agriculture. This is important for sustainability and reducing our carbon footprint.
- Improving efficiency: By making use of all by-products, we can improve the efficiency of animal agriculture and make it more cost-effective. This can help to reduce the overall cost of animal products for consumers.
- Maximizing profits: By utilizing all parts of an animal, we can maximize profits for farmers and producers. This is important for the economic sustainability of the animal agriculture industry.
- Providing valuable resources: By-products such as bones, hides, and feathers can be used to produce a variety of products, including fertilizer, leather, and bedding. These products provide valuable resources for other industries and can help to reduce our reliance on non-renewable resources.
- Supporting local economies: By utilizing all by-products, we can support local economies and create jobs in a variety of industries, including leather production, pet food manufacturing, and fertilizer production.
- Reducing environmental pollution: By-products such as manure and waste water from animal processing can be treated and used for agricultural purposes, such as fertilizing crops. This reduces the amount of pollution and waste that is released into the environment, which is important for protecting the health of ecosystems and human populations.
- Meeting nutritional needs: By utilizing all parts of an animal, we can provide a wider range of nutrients and minerals to consumers. By-products such as liver and bone marrow, for example, are rich in iron and calcium, respectively. Including these by-products in the human diet can help to meet nutritional needs and improve overall health.
- Supporting animal welfare: By utilizing all parts of an animal, we can reduce the need for intensive farming practices, which can be detrimental to animal welfare. By maximizing the value of each animal, we can reduce the overall number of animals that need to be raised and processed, which can lead to more humane farming practices.
- Reducing the risk of disease: By properly processing and utilizing all animal by-products, we can reduce the risk of disease transmission between animals and humans. Proper handling and processing of by-products can help to ensure that any potential pathogens are eliminated and that the final products are safe for consumption or use.
Consequences of failure to ensure complete value addition of all animal by-products
The failure to ensure complete value addition of all by-products derived from animals can have several negative consequences, including:
- Environmental pollution: When animal by-products are not properly processed or utilized, they can contribute to environmental pollution. For example, animal waste that is not properly treated can contaminate soil and water, leading to environmental degradation and health risks for human and animal populations.
- Economic losses: The failure to utilize all by-products can result in economic losses for farmers and producers. This is because valuable resources are wasted and not utilized for other purposes, such as the production of fertilizer or leather.
- Animal welfare concerns: If by-products are not properly utilized, it may result in the need for more animals to be raised and processed to meet demand. This can lead to more intensive farming practices and potential animal welfare concerns.
- Health risks: Failure to properly process animal by-products can lead to health risks for both animals and humans. For example, if animal waste is not properly treated, it can harbor pathogens that can cause disease in both animals and humans.
- Wasted potential as nutritious food sources: By-products are highly nutritious and their utilization has potential to advance the fight against food nutrition insecurity.
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions: When animal by-products are not utilized, they can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, such as methane, which is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. This is because animal waste that is not properly treated can release methane into the atmosphere.
- Decreased food security: When animal by-products are not utilized, it may lead to increased demand for other sources of protein, such as plant-based proteins. This can have implications for food security, particularly in areas where plant-based protein sources may not be readily available or accessible.
- Reduced quality of life: The failure to properly utilize animal by-products can have negative impacts on the quality of life for both human and animal populations. For example, when animal waste is not properly treated, it can lead to unpleasant odors and decreased air quality, which can negatively impact the quality of life for nearby residents.
Our Blog ↗
Read the latest from our blog
Ask a Question ↗
Ask a question and get answers from our community
Give Feedback ↗
We value your feedback.

