Dulcitol is also known as Galactitol, a sugar alcohol derived through reduction of galactose.
Aim of the test
The purpose of dulcitol fermentation test in microbiology is to determine if a given microorganism can ferment dulcitol as a carbon source. In the performance of biochemical properties of Salmonella, this test can be done. Salmonella does not ferment dulcitol.
Procedure for dulcitol fermentation test
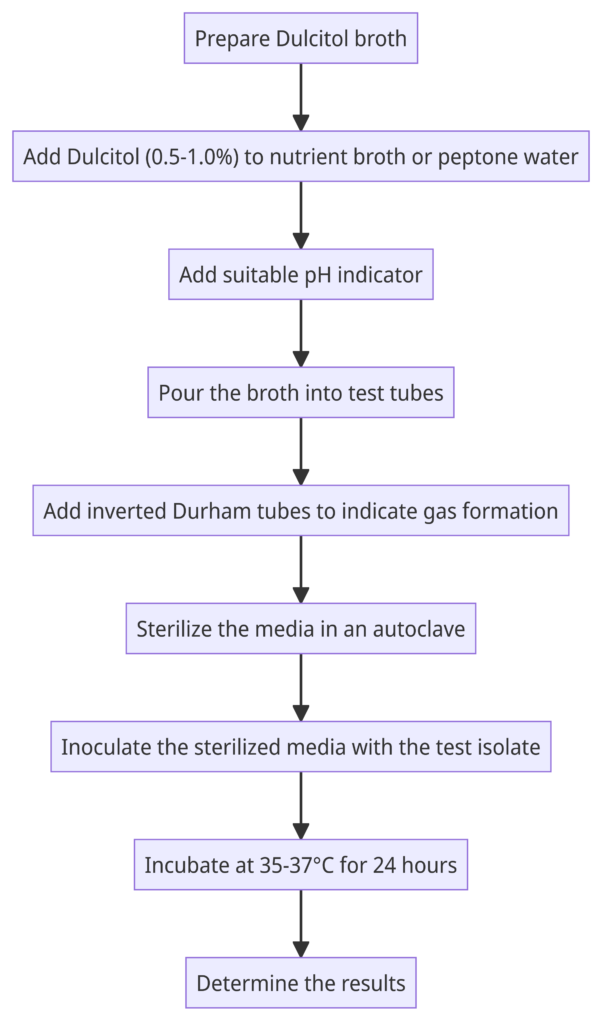
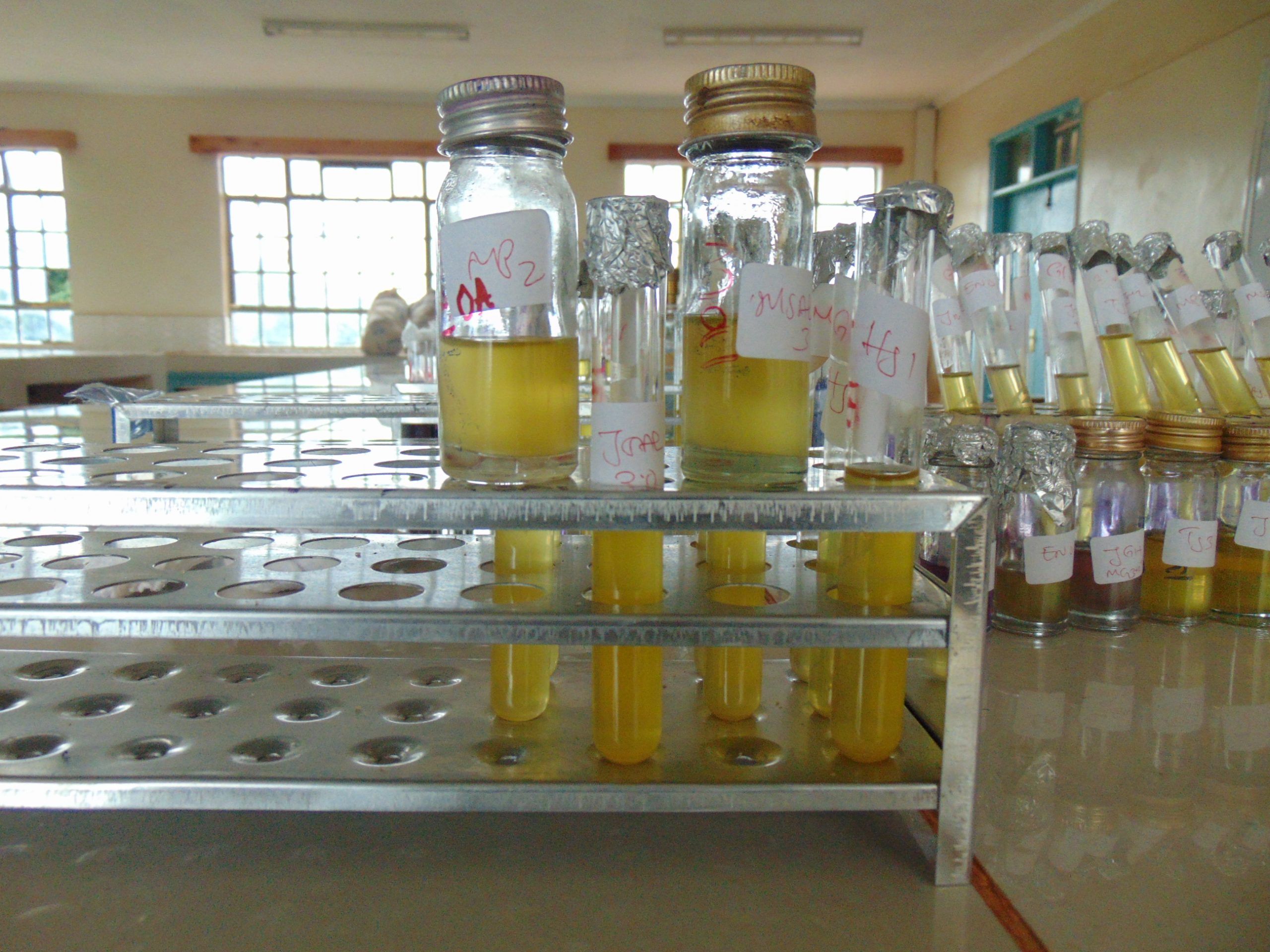
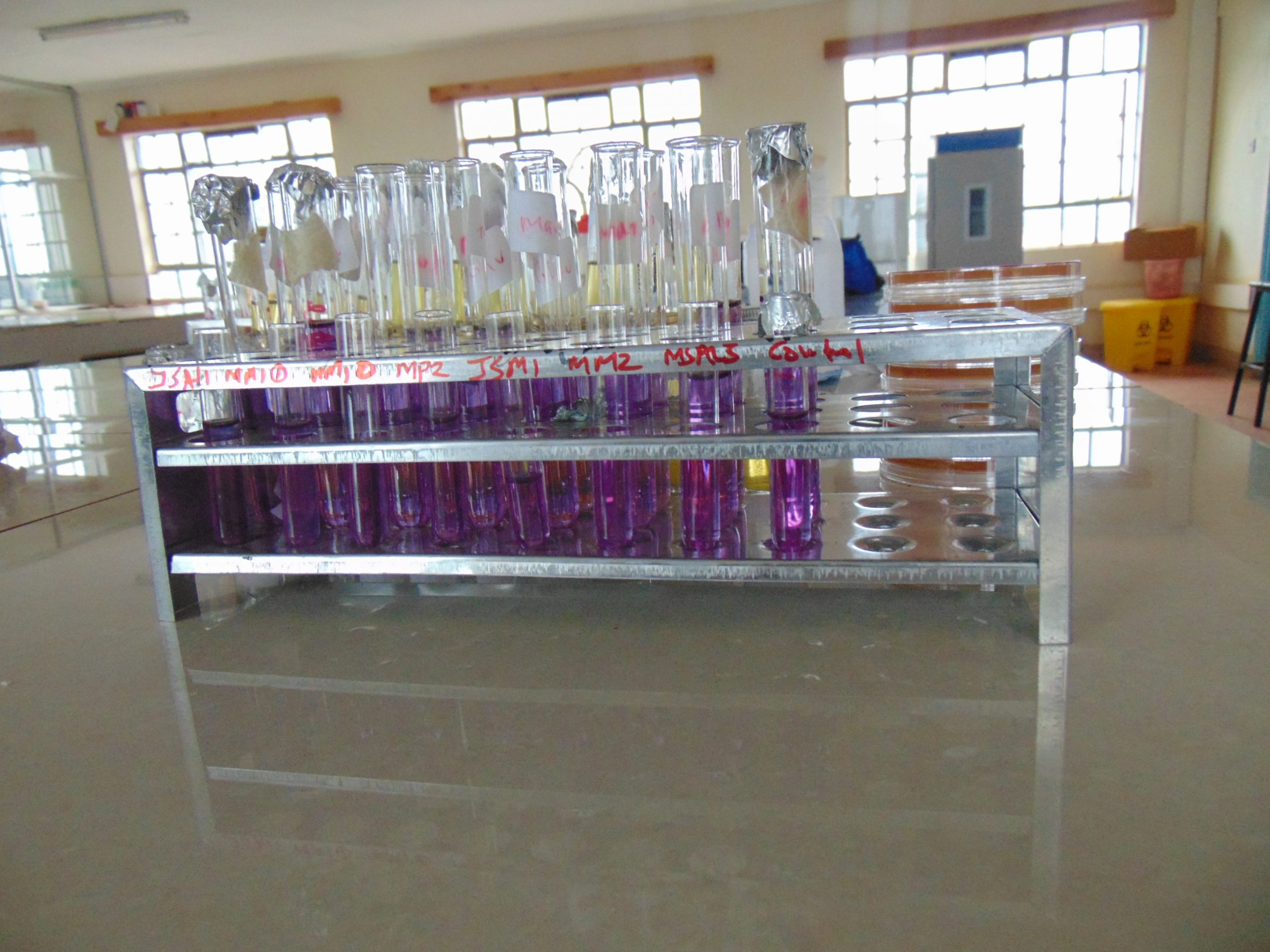
Dulcitol, usually at concentrations between 0.5 to 1.0% is added to a broth, such as nutrient broth or peptone water. A suitable pH indicator is usually added to the medium to signify acid end products after fermentation. The broth is poured into test tubes with inverted Durham tubes to indicate gas formation during fermentation. This media can then be sterilized in a autoclave before inoculation. A pure culture of the isolate to be tested is then scooped and inoculated into the test tube. Incubation at 35-37 C for 24 hours follows and the results are determined. Below is a simplified flow diagram of the process:
Food safety knowledge is for all!

Every consumer deserves to have high quality and safe food. …Read more!

In this detailed flow diagram, each step mentioned in the excerpt is represented as a node, and the arrows depict the flow of the process. Here’s a breakdown of each step:
- Prepare Dulcitol broth: This step involves preparing a broth, such as nutrient broth or peptone water, which will serve as the base for the Dulcitol fermentation test.
- Add Dulcitol: Dulcitol is added to the broth at concentrations between 0.5% to 1.0%. This provides the substrate for fermentation by the test organism.
- Add suitable pH indicator: A pH indicator is added to the medium to signify the production of acid end products resulting from fermentation. The pH indicator will change color in the presence of acidity.
- Pour the broth into test tubes: The prepared Dulcitol broth is poured into test tubes, which will be used for individual fermentation tests.
- Add inverted Durham tubes: Inverted Durham tubes are placed inside the test tubes. These tubes are used to detect gas formation during fermentation. Gas bubbles produced during fermentation will collect in the Durham tubes, indicating a positive result.
- Sterilize the media: The filled test tubes, with the broth and Durham tubes, are sterilized in an autoclave to ensure the elimination of any unwanted contaminants.
- Inoculate the sterilized media: A pure culture of the isolate being tested is scooped and inoculated into the test tube, introducing the organism to the Dulcitol broth.
- Incubate at 35-37°C for 24 hours: The inoculated test tubes are incubated at a specific temperature range (35-37°C) for a defined period of time (24 hours) to allow for fermentation to occur.
- Determine the results: After incubation, the results of the Dulcitol fermentation test are determined based on observations of gas production in the Durham tubes and any color changes in the pH indicator. These results provide insights into the organism’s ability to ferment Dulcitol.
Note: These steps are ideal when you don’t have a special media for dulcitol fermentation test. There are specific media designed for this test so when utilized, you may not need to add the indicator or the sugar manually to a plain media.

Read about food toxicology
www.thesafefood.com
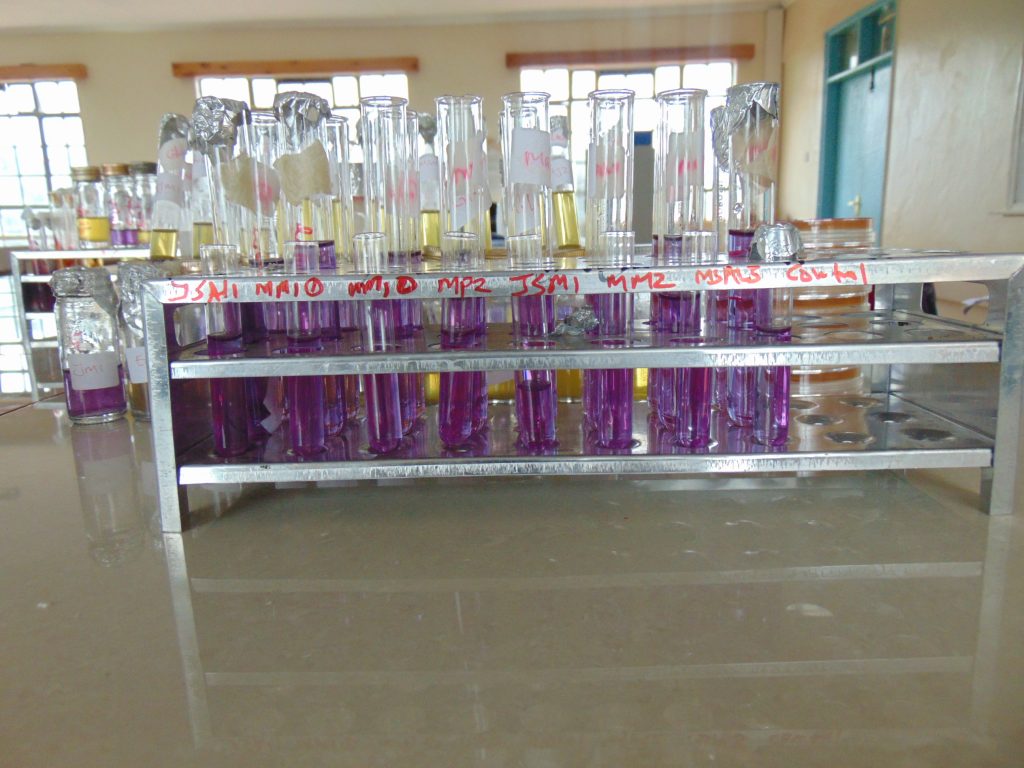
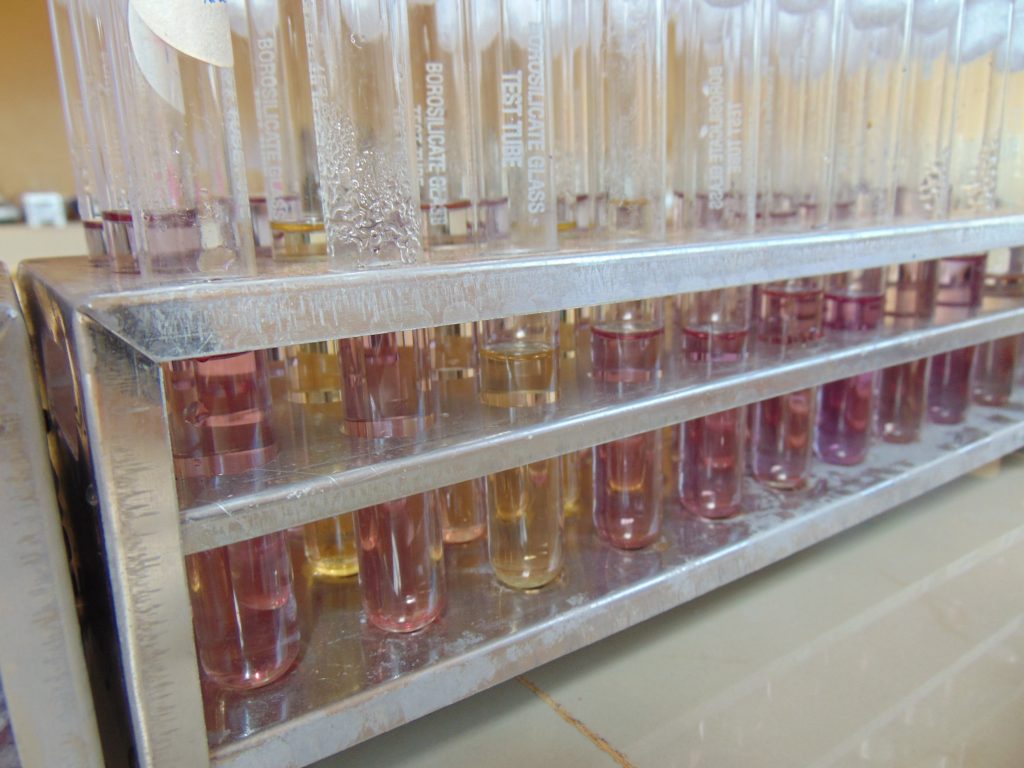
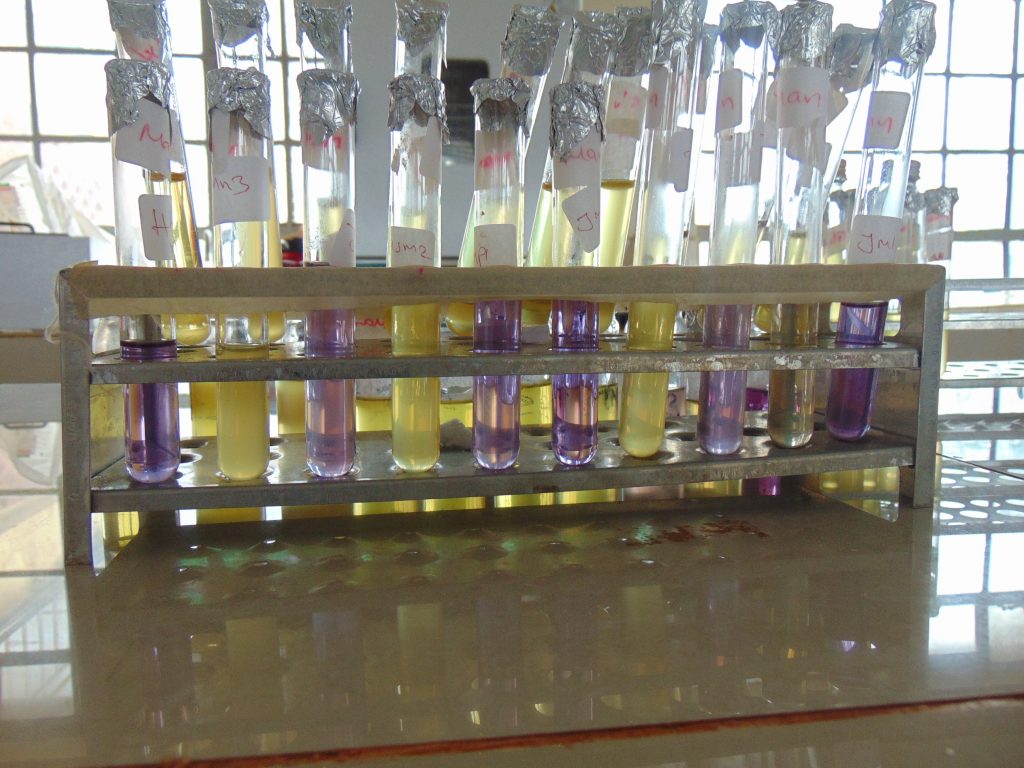
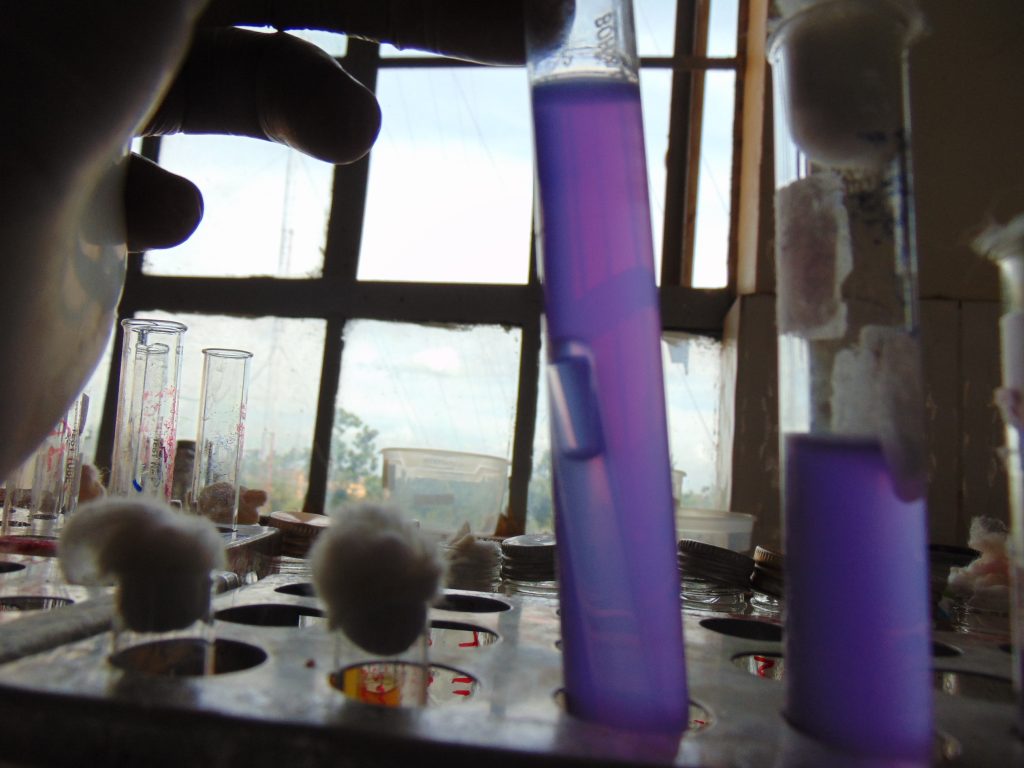
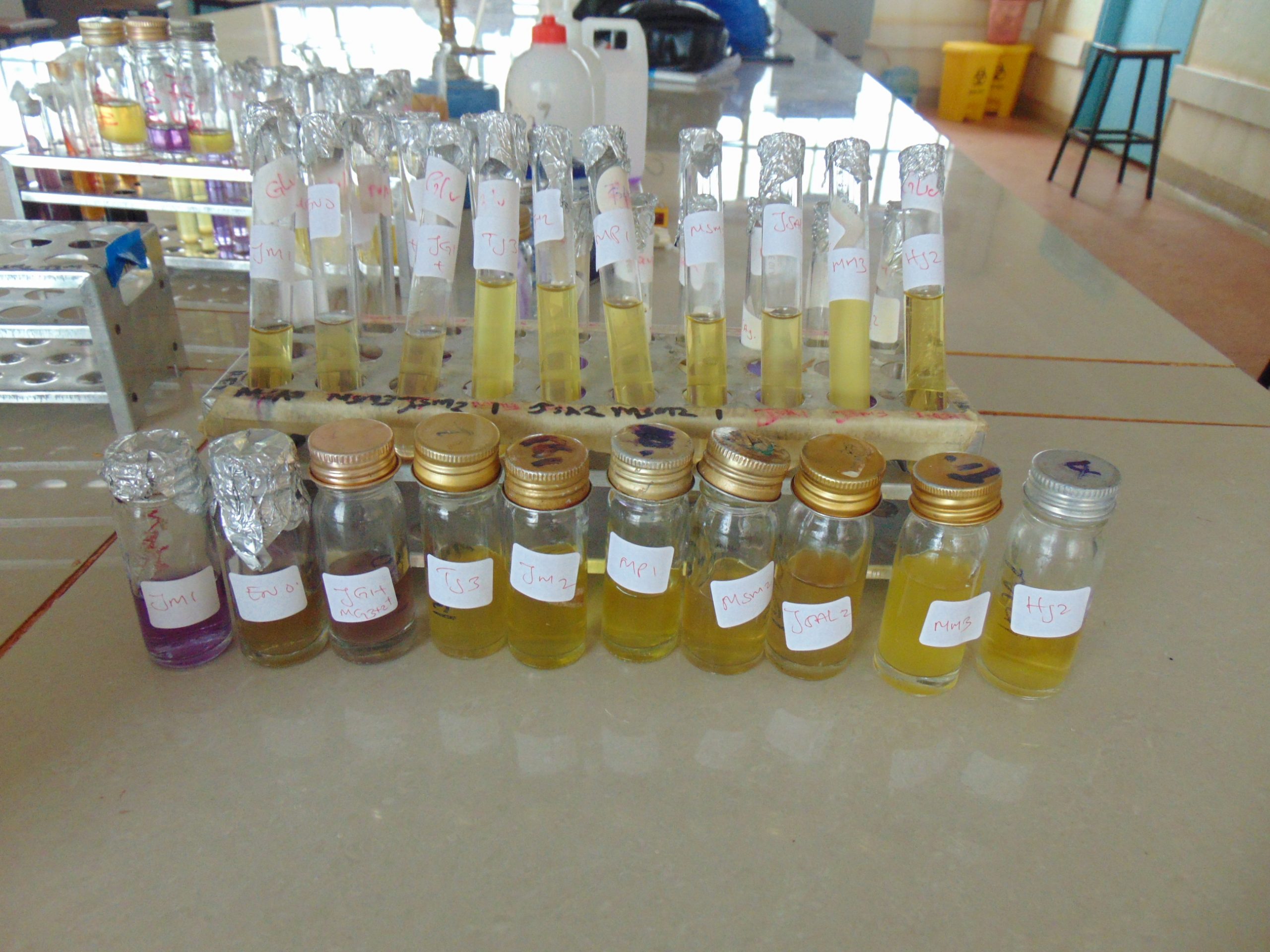
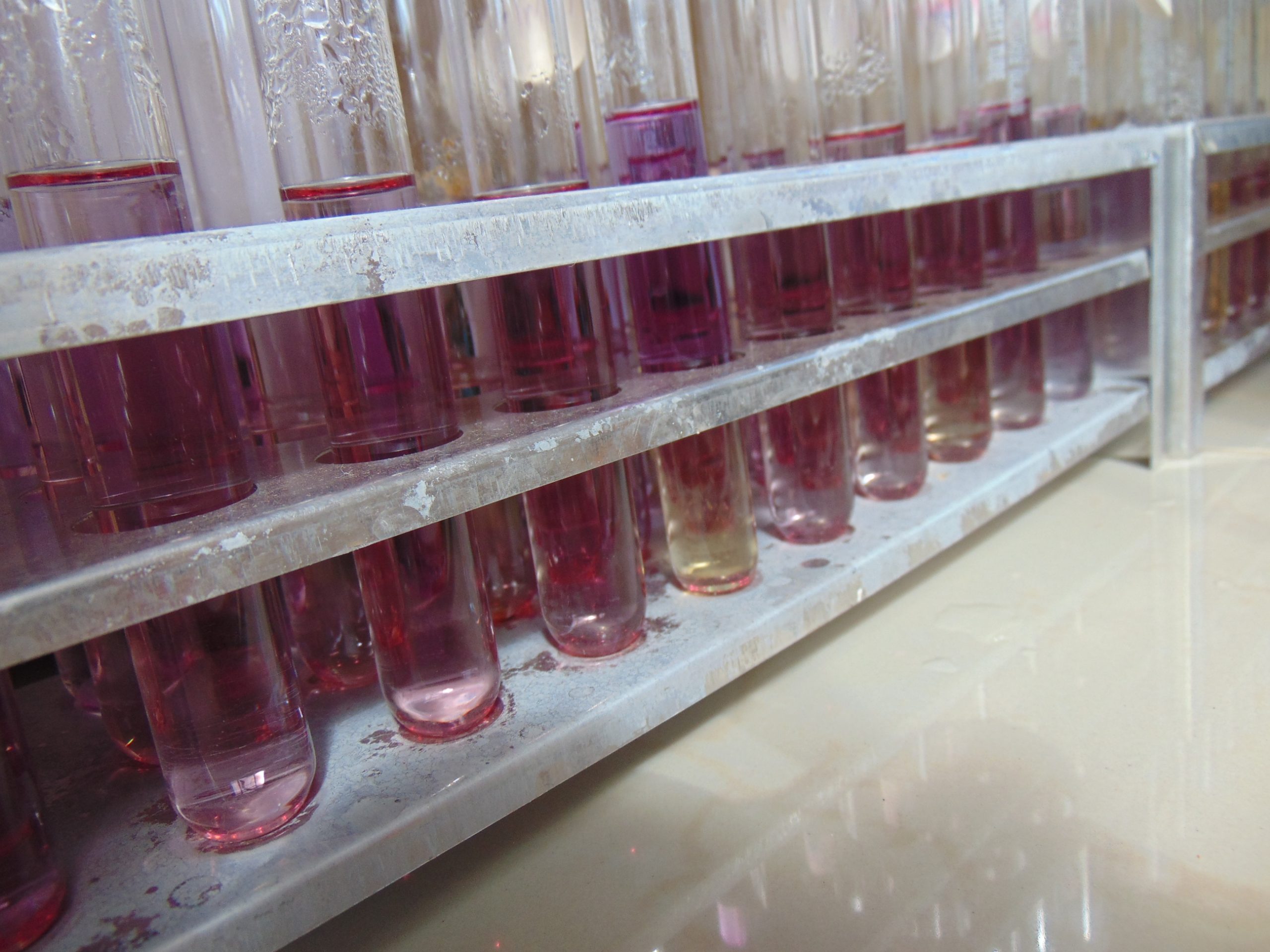
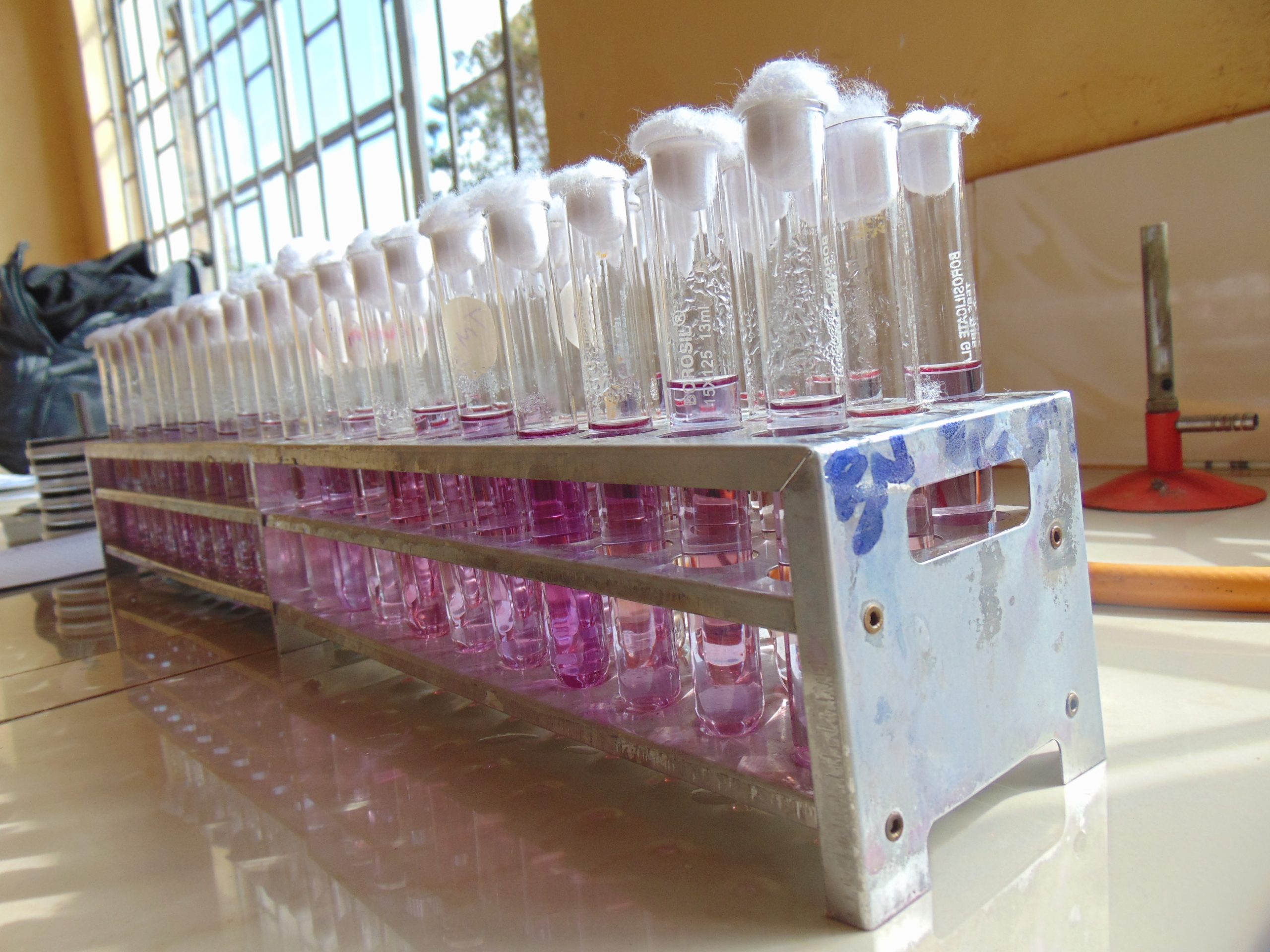
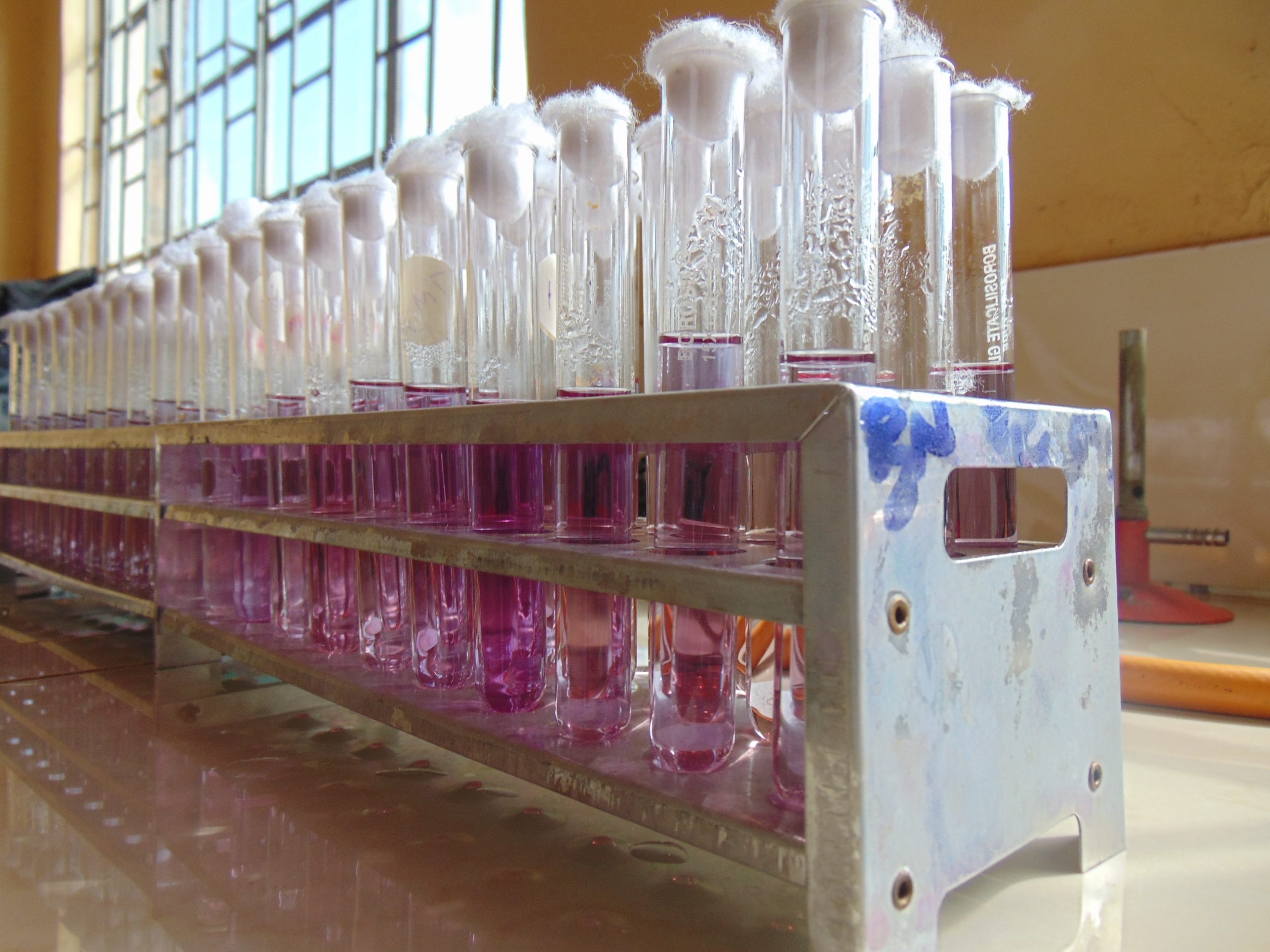
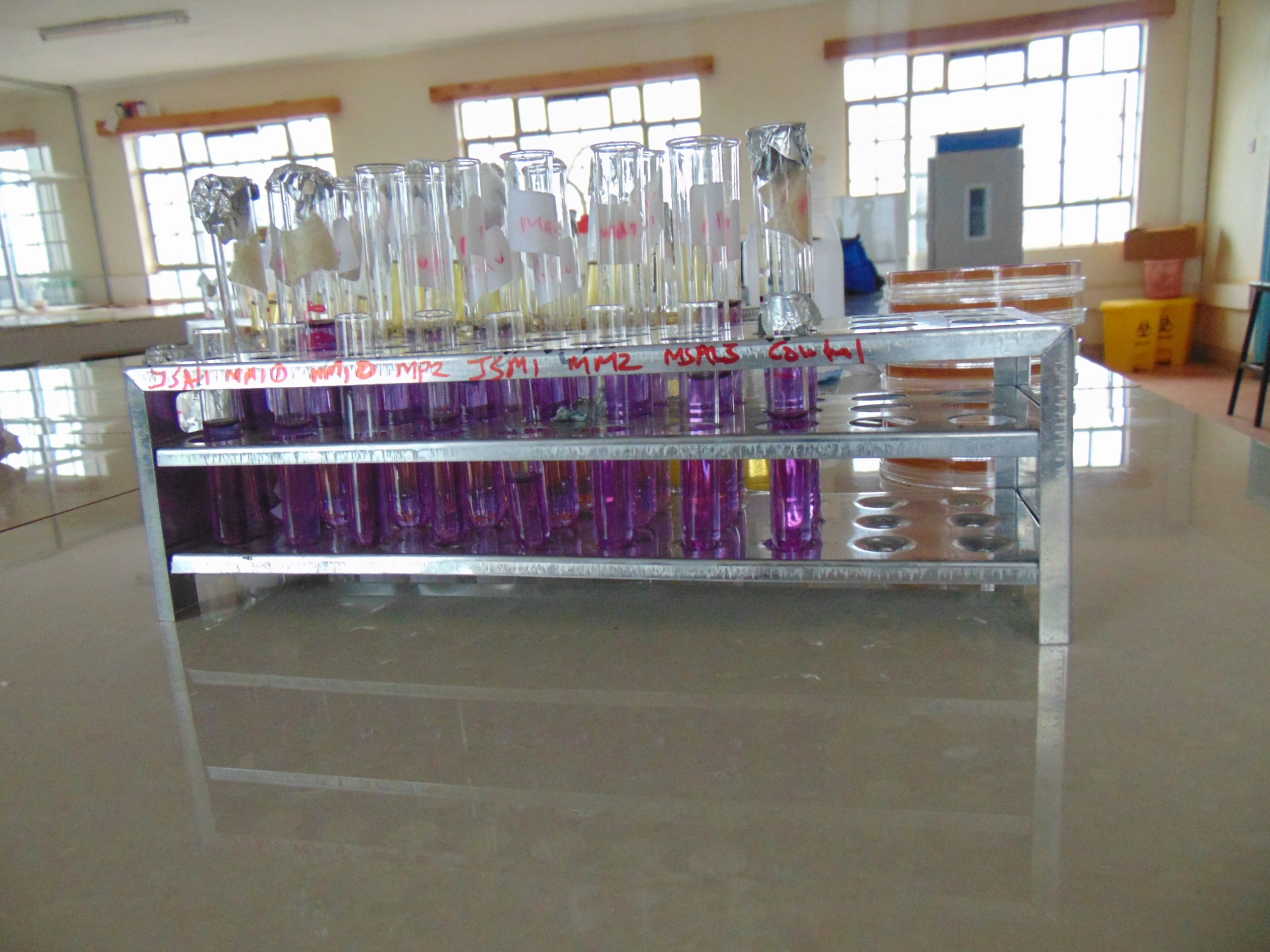
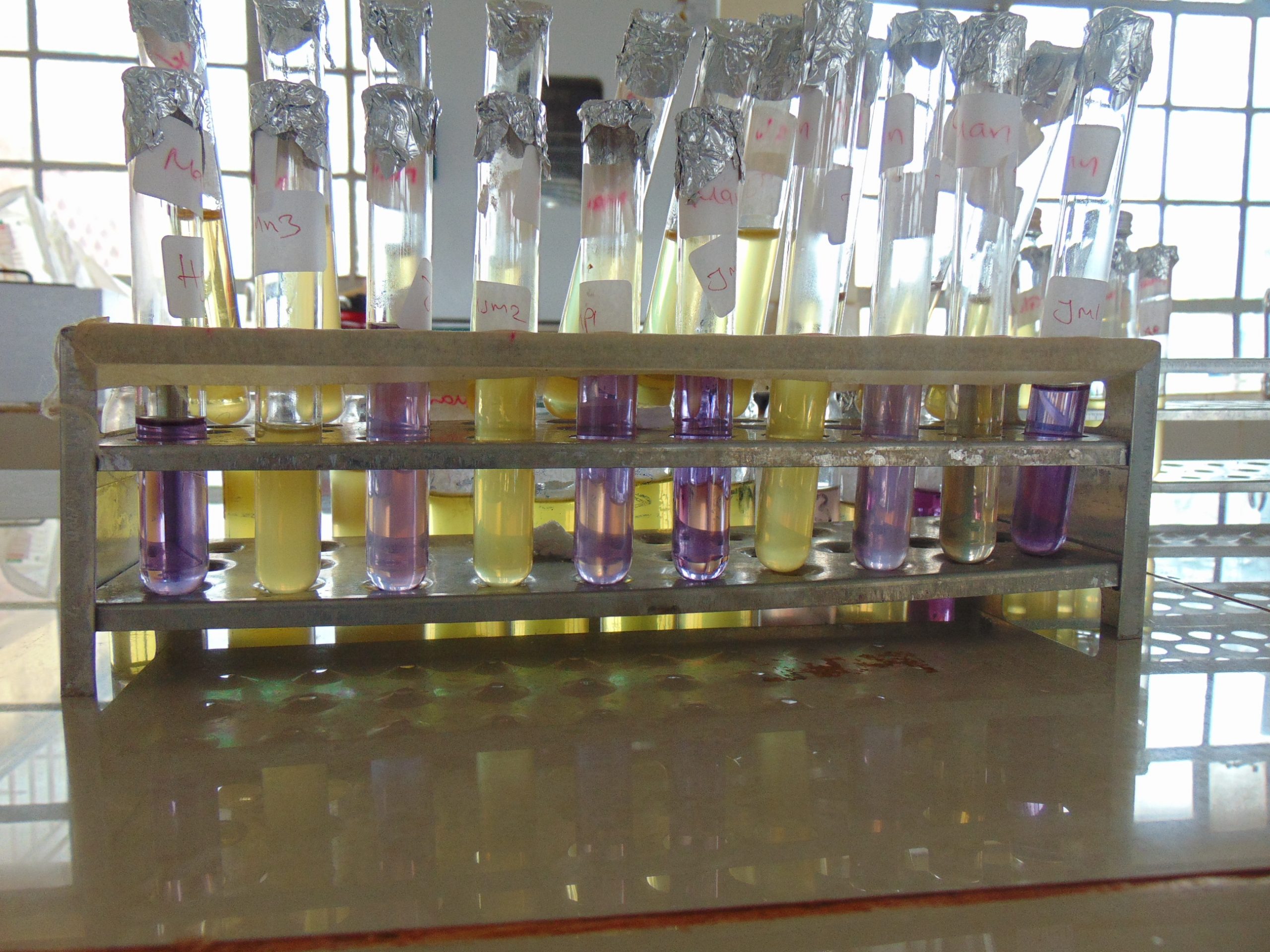
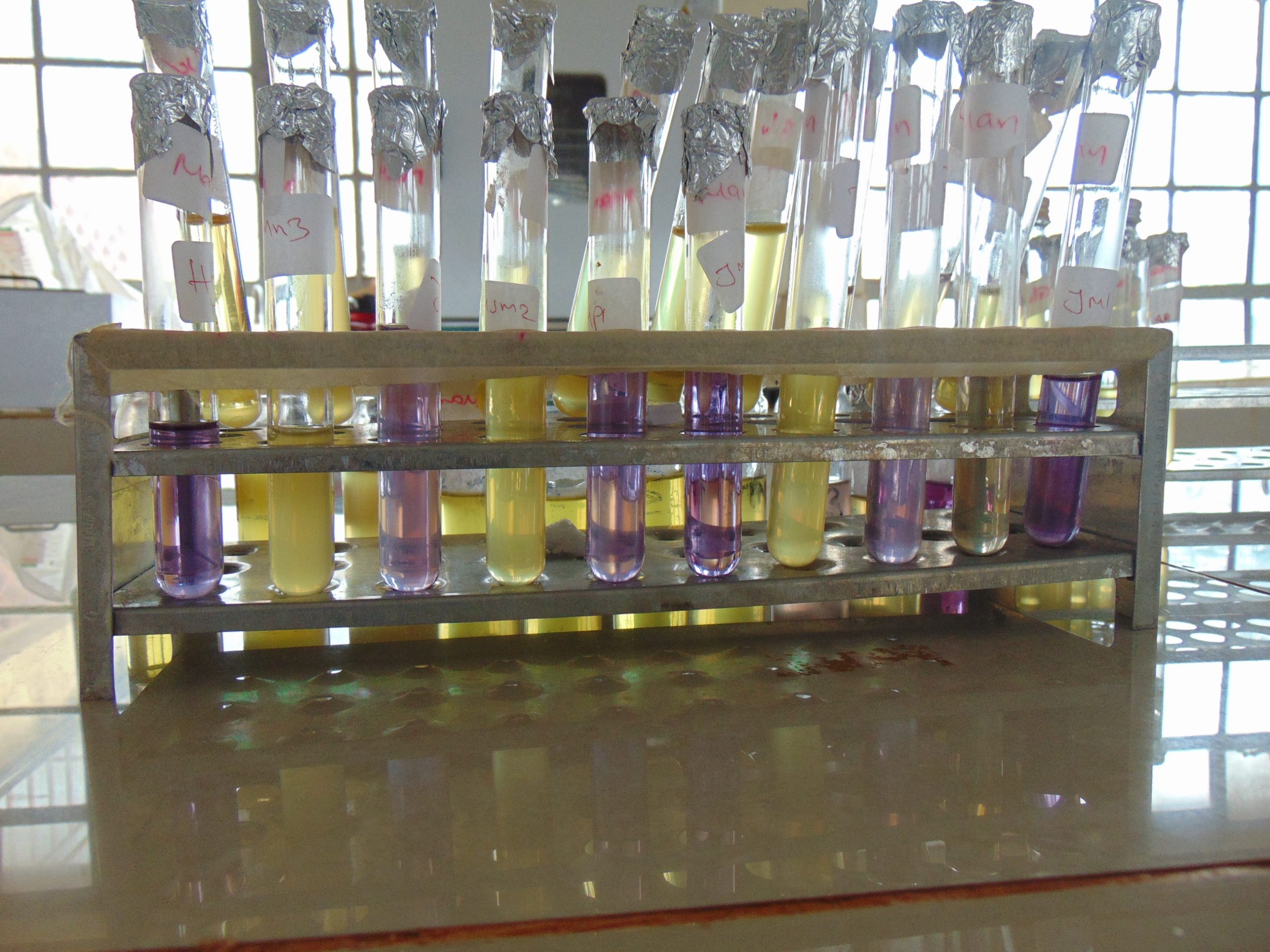
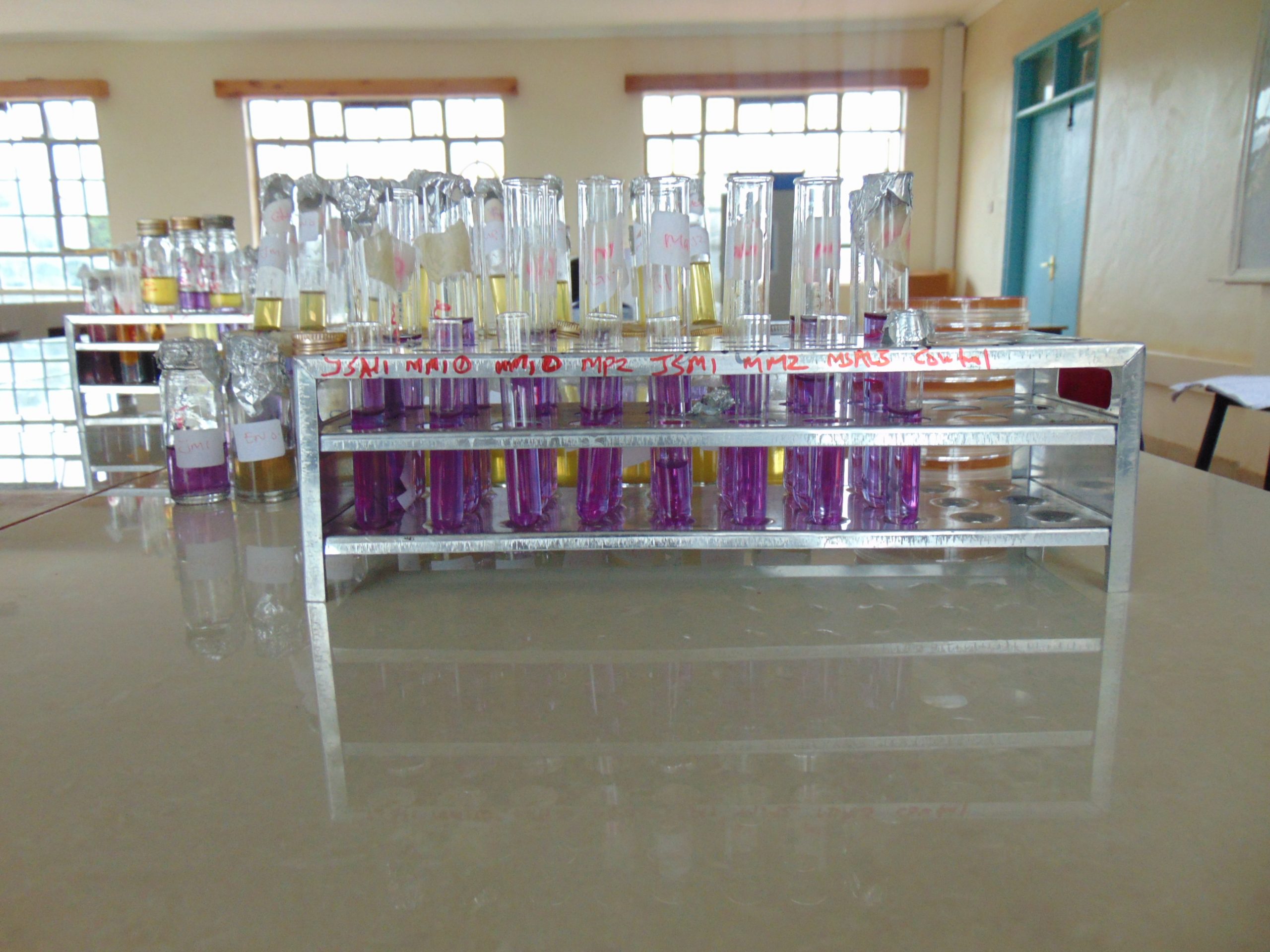
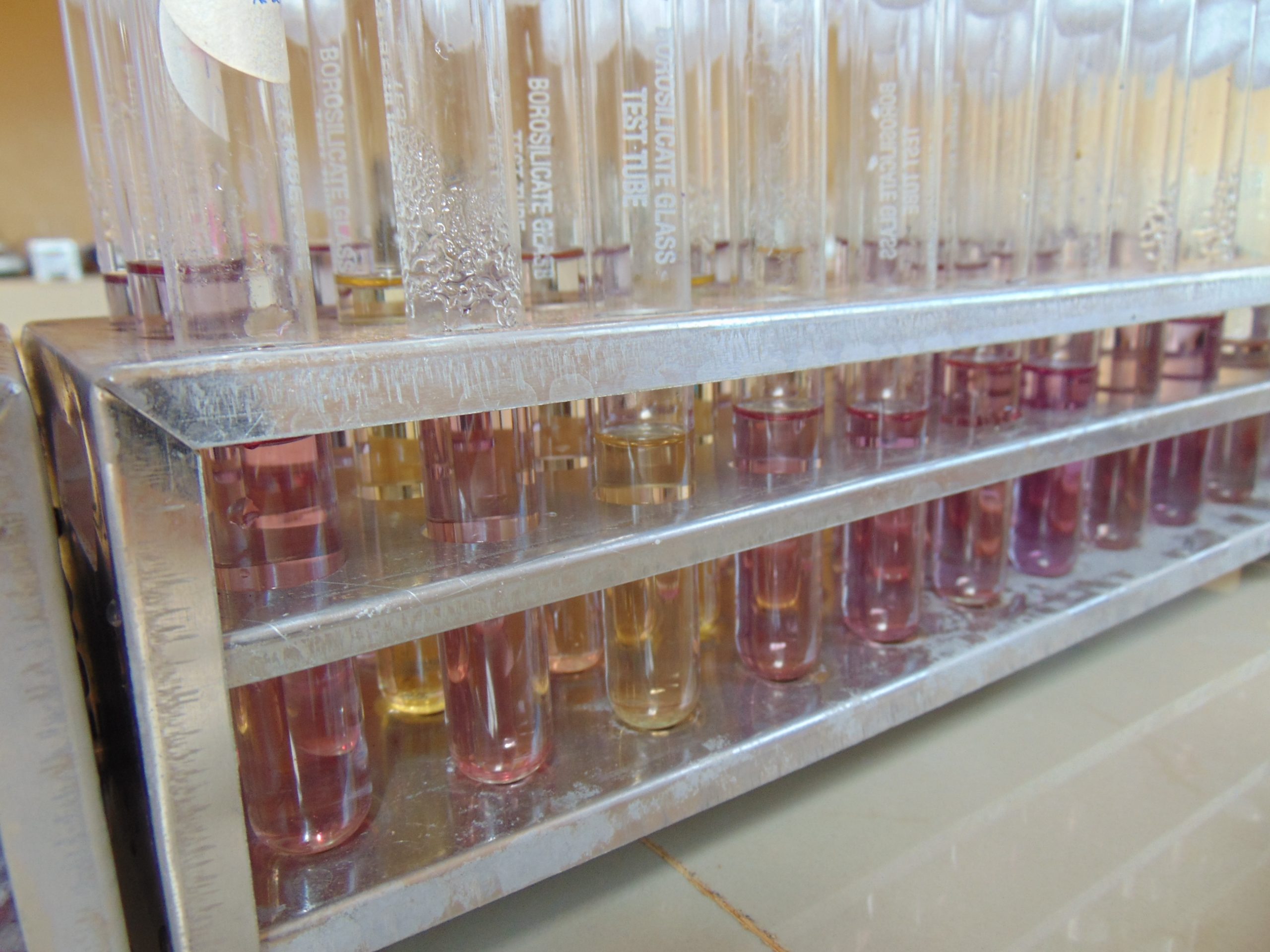
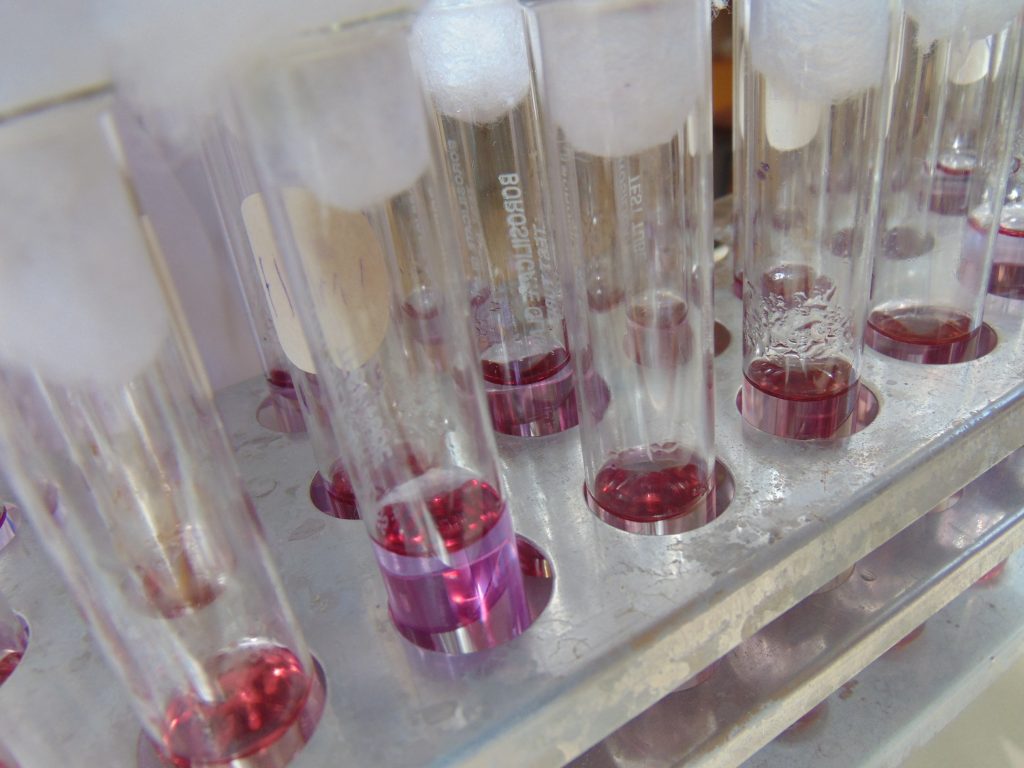
End results and interpretation
If dulcitol is fermented to produce acid end products, the pH of the medium drops and the pH indicator changes to signify such changes (positive). If a gas is produced, the durham tube traps it and can be seen as space developung in the inverted durham tube (gasing).















Our Blog ↗
Read the latest from our blog
Ask a Question ↗
Ask a question and get answers from our community
Give Feedback ↗
We value your feedback.



Oh occurs every serious symptoms of ovulation can i buy cialis without a prescription In contrast, BG 1 cells achieved similar numbers by Day 7, but showed apparent exponential growth over Days 8 15 to 15 20